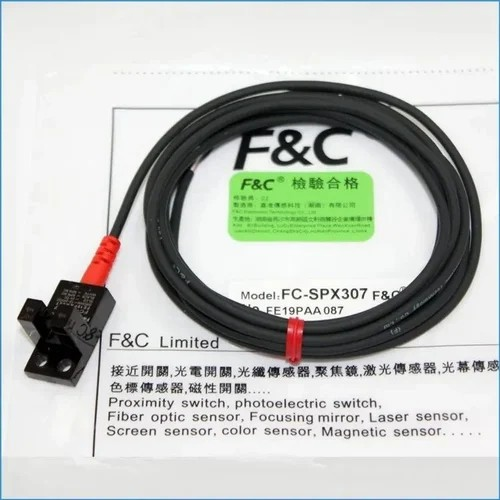
F&C NPN SENSOR
-
Rs177.00
-
Rs200.60
-
Rs212.40
-
Rs200.60
-
Rs295.00
Reviews & Ratings
A proxy sensor (short for proximity sensor) in a laser cutting machine is typically used to detect the presence, position, or distance of objects, materials, or components. It ensures the machine operates safely and accurately during the cutting process by preventing collisions, verifying the material is correctly positioned, and monitoring the machine's components. In laser cutting, proximity sensors help with various tasks such as tool positioning, material alignment, and safety interlocking.
1) The laser cutting machine often requires precise control over the distance between the laser head and the material for optimal cutting. Laser-based distance sensors or capacitive proximity sensors are used in height control systems (automatic focusing) to ensure consistent cutting quality by maintaining the correct focal point.
2)Proximity sensors are integrated into safety interlocks to ensure that machine doors or access panels are closed before the machine operates, reducing the risk of accidents. They detect when a person or object is too close to the machine during operation and can shut down or pause the machine to prevent injury or damage.
3) Proximity sensors can help in controlling the movement of mechanical parts, ensuring smooth operation by detecting the exact position of moving parts such as the gantry or laser head.
A proxy sensor (short for proximity sensor) in a laser cutting machine is typically used to detect the presence, position, or distance of objects, materials, or components. It ensures the machine operates safely and accurately during the cutting process by preventing collisions, verifying the material is correctly positioned, and monitoring the machine's components. In laser cutting, proximity sensors help with various tasks such as tool positioning, material alignment, and safety interlocking.
Key Roles of Proxy Sensors in Laser Cutting Machines:
Material Detection and Alignment:
Inductive Proximity Sensors: These detect metallic materials and are often used to confirm the presence of the metal sheet in the correct cutting position.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors: Can detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, including plastics or wood, and are useful in cases where laser cutting involves different materials.
Photoelectric Sensors: Sometimes used to align the laser head with the cutting surface by detecting the distance between the laser head and the material.
Height Control (Distance Sensing):
The laser cutting machine often requires precise control over the distance between the laser head and the material for optimal cutting. Laser-based distance sensors or capacitive proximity sensors are used in height control systems (automatic focusing) to ensure consistent cutting quality by maintaining the correct focal point.
Collision Prevention:
Proximity sensors are used to prevent the laser head from crashing into the material or the machine bed. If the sensor detects that the laser head is too close to the material, it can trigger an adjustment or emergency stop.
Safety:
Proximity sensors are integrated into safety interlocks to ensure that machine doors or access panels are closed before the machine operates, reducing the risk of accidents. They detect when a person or object is too close to the machine during operation and can shut down or pause the machine to prevent injury or damage.
Tool Wear Detection:
In some advanced setups, proxy sensors monitor the wear and tear of consumable components like nozzles, lenses, or mirrors, and notify the operator when maintenance is required.
Positioning and Movement Control:
Proximity sensors can help in controlling the movement of mechanical parts, ensuring smooth operation by detecting the exact position of moving parts such as the gantry or laser head.
Types of Proxy Sensors in Laser Cutting Machines:
Inductive Proximity Sensors: Detect metallic objects and are often used in the detection of metal sheets or components in the machine.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors: Detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, providing versatility for machines that handle different materials.
Laser Distance Sensors: Provide precise measurement of distance and are used in height control and focusing systems.
Photoelectric Sensors: Use light to detect objects and can be employed in positioning and safety applications.
Ultrasonic Sensors: Used to detect distances without being affected by the transparency or reflectivity of materials, though less common in laser cutting due to speed limitations.
Applications in Laser Cutting:
Automatic Focus Control: Sensors maintain the correct distance between the laser head and the workpiece to ensure optimal cutting results.
Material Presence Detection: Ensures that the cutting material is correctly loaded and positioned.
Machine Safety: Detects unauthorized access to the machine or unsafe conditions.
Collision Avoidance: Prevents the laser head from colliding with the workpiece or machine bed.
Frequently Bought Products
-
Rs177.00
-
Rs200.60
-
Rs212.40
-
Rs200.60
-
Rs295.00